Solar Energy Solutions: How Does Solar Compare to Other Renewable Energy Sources?
As the world moves more and more towards sustainability, we have turned our attention to the massive sources of clean energy solutions available around us in nature – sun, wind, water, and biomass in particular. There was never any doubt about the magnitude of these, though the challenge was always in harnessing them.
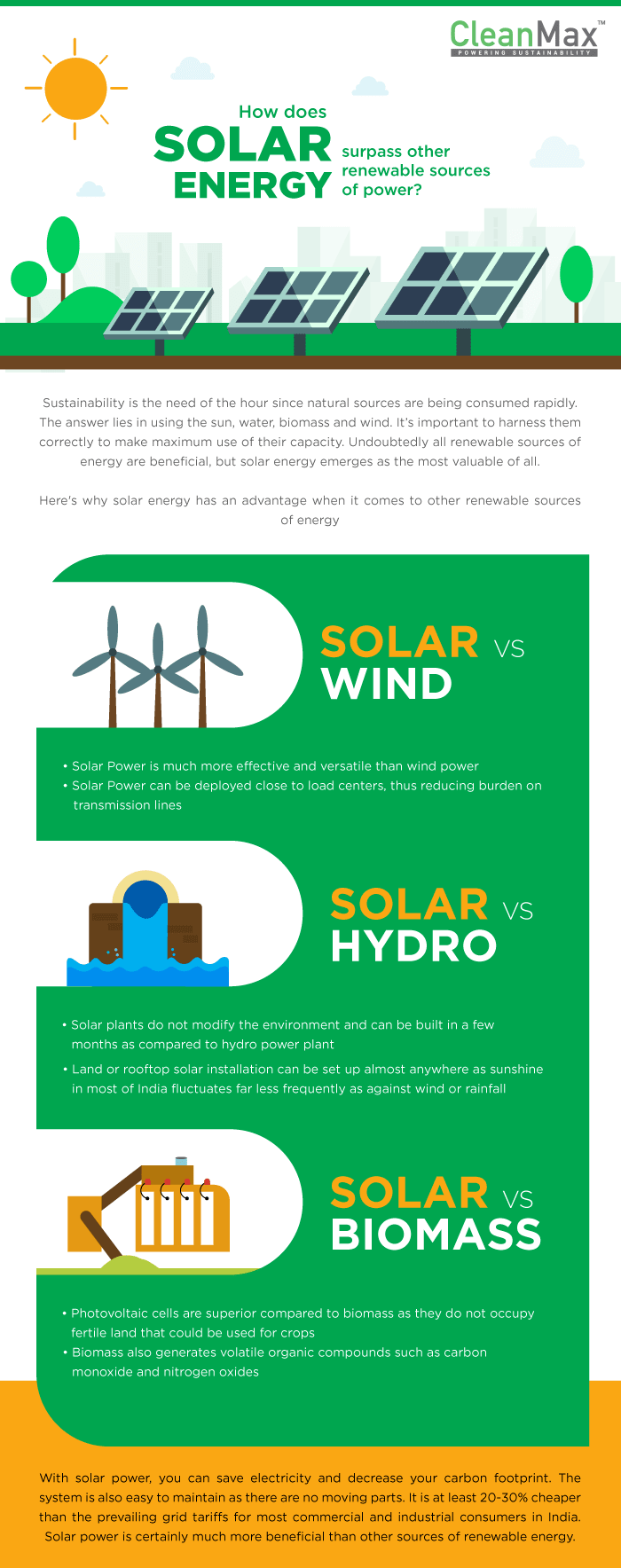
Here, we explain how solar energy stacks up against other forms of renewable energy.
Solar Energy versus Wind
Despite wind technology being in the market for a long time, it has experienced some issues. The initial power gathered from wind is less expensive to produce, but wind turbines require much more maintenance than photovoltaic cells. Also, wind generating plants are set up at distant locations, with little or no access to the actual consumer. The discoms (distribution companies), for the fear of losing business, have levied huge wheeling charges over the years, which has made the proposition unviable in recent times.
They are also more disruptive than their solar counterpart, since they are prone to making lots of noise.
Solar Energy versus Hydro
Hydroelectricity, though effective, is generally supplied through the use of large dams which also mean initial installation cost will be very high. Also, building a dam has the ability to alter an entire ecosystem. Hydro plants often change the natural flow of the waterways they take over, creating new lakes and reducing water flow downstream. These installations can also affect wildlife in the area, blocking fish migration and altering habitats.
Photovoltaic panels, on the other hand, do not change the environment and are small in comparison to dams. One of the advantages of solar power is its versatility. A land or roof installation can be set up in regions that many would think don’t receive enough sunlight.
Solar Energy versus Biomass
Burning biomass to generate electricity has some appeal as biomass is renewable in some sense. However, the logistics and overall energy balance undermine this argument, as a lot of energy – mostly oil based – is required to harvest and move the crops to the power station.
The use of biomass, such as the burning of wood, waste, alcohol fumes, or landfill gases produces less waste energy than fossil fuels or coal. Unfortunately, biomass creates volatile organic compounds like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. On the positive side, its pollution is modest in comparison to traditional fuels. Photovoltaic cells prove superior again in that they create no emissions and do not require land that could be used for crops.
In addition, solar panels have efficiencies as high as 19%, meaning that much of the sun’s energy is converted into electricity. The efficiency of biomass is much, much lower – perhaps less than 1%. Solar energy is at par with the grid tariffs for most commercial and industrial consumers in India. If you’ve been thinking about going solar, now is the time to make the change. Government financial incentives are still ripe for the picking, and you stand to gain a lot as one of the early adopters of solar energy. Adding solar power plant in your factory is an excellent project for several reasons: You’ll save loads on electricity, you’ll reduce your carbon footprint; and if you’re installing in a remote location (such as a cabin), you’ll have much less to worry about than you would with a gasoline generator. You’ll also support a growing industry, and in doing so, help contribute to the worldwide adoption of this wonderful new energy source.
For more details, Contact Us or write to [email protected]